Abstracts from the 29^ National Conference of the Italian Society for the Study of Hemostasis and Thrombosis, Bergamo, Italy | 23-25 October 2025
Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
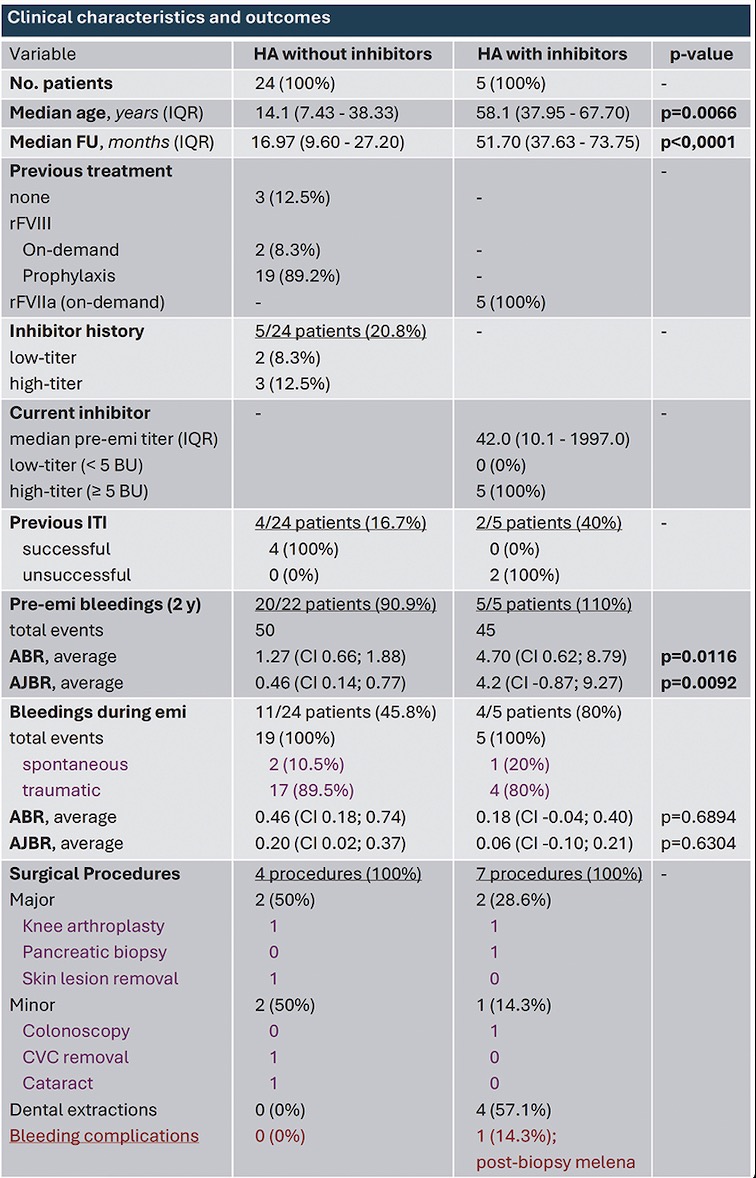
PO24 | Emicizumab prophylaxis and bleeding outcomes: a single center clinical experience
A. Taglietti1, S. Ligia1, F. Paoletti1, R. Mormile1, E. Baldacci2, A. Chistolini1, C. Santoro1,2 | 1Hematology, Department of Translational and Precision Medicine, Sapienza University of Roma; 2Hematology, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Policlinico Umberto I, Roma, Italy
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Published: 22 October 2025
392
Views
0
Downloads
Similar Articles
- PO83 | A case of deep vein thrombosis in a patient with systemic mastocytosis , Bleeding, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
- PO22 | Early detection and management of PICC-related thrombosis in oncohematologic patients through serial ultrasound monitoring: a prospective observational study , Bleeding, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
- PO51 | Thrombocythemia associated with a non-canonical JAK2 mutation: a case report , Bleeding, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
- PO84 | Beyond the scores: unmasking a silent pulmonary embolism in essential thrombocythemia , Bleeding, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
- PO23 | Plasmic score applicability for the diagnosis of thrombotic microangiopathy associated with acquired ADAMTS13 deficiency in emergency settings at the hub laboratory of AUSL Romagna: state of the art and future prospects , Bleeding, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
- PO52 | Comprehensive assessment of variables affecting spontaneous platelet aggregation , Bleeding, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
- PO85 | Acute retinal ischemia in hemoglobin SC disease: a case report and review of the literature , Bleeding, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
- PO25 | Baseline thrombin generation test does not predict thrombotic events in acute leukemia: a monocentric prospective study , Bleeding, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
- PO53 | Effectiveness and safety of DOACS in patients with renal transplantation , Bleeding, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
- PO86 | Emicizumab in patients with moderate hemophilia A and severe bleeding phenotype: single-center real-world experience , Bleeding, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Vol. 4 No. s1 (2025)
1-10 of 96
Next
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.